Iron Ore Processing Flow Chart: Step-by-Step Guide
 Laura
Laura
 Feb 13, 2026
Feb 13, 2026
 14
14
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!

Iron ore magnetic separation beneficiation site
Iron ore processing is a critical stage in the mining and steel manufacturing industries. From raw ore extraction to producing a high-grade iron concentrate, each step plays a vital role in efficiency, product quality, and cost control. Understanding the iron ore processing flow chart helps mining professionals, engineers, and investors visualize the entire process and identify opportunities for optimization.
This step-by-step guide explains each stage of iron ore processing in a clear and structured way.
01What Is an Iron Ore Processing Flow Chart?
BackAn iron ore processing flow chart is a visual representation of the sequence of operations involved in converting mined iron ore into usable material. It outlines the movement of ore through crushing, grinding, separation, and concentration stages, showing how raw material becomes a refined product ready for steelmaking.
Flow charts are used to:
Design and optimize processing plants
Improve operational efficiency
Reduce energy and water consumption
Identify bottlenecks in production
02Step 1: Iron Ore Mining and Extraction
BackThe process begins with the extraction of iron ore from open-pit or underground mines. The type of mining method depends on the ore body’s depth, size, and geological conditions.
After drilling and blasting, large chunks of iron ore are transported to the processing plant by haul trucks or conveyor systems.
03Step 2: Crushing and Screening
BackCrushing is the first major step in the iron ore processing flow chart. The mined ore is reduced in size using crushers such as:
Jaw crushers
Gyratory crushers
Cone crushers
After crushing, the material passes through vibrating screens to separate fine particles from larger ones. Oversized material is returned to the crusher for further size reduction.
Purpose of crushing and screening:
Prepare ore for grinding
Improve separation efficiency
Reduce equipment wear downstream
04Step 3: Grinding and Classification
BackIn this stage, crushed iron ore is ground into fine particles using grinding equipment such as ball mills or rod mills. Water is often added to create a slurry.
Classification equipment like hydrocyclones or spiral classifiers separates fine particles from coarse ones. Coarse material is sent back for further grinding, while fine material moves forward in the process.
Key benefits of grinding:
Liberates iron minerals from waste rock
Improves separation accuracy
Enhances concentrate quality
05Step 4: Iron Ore Beneficiation and Separation
BackBeneficiation is one of the most important stages in the iron ore processing flow chart. It removes impurities and increases iron content using various separation techniques, including:
1. Magnetic Separation
Magnetic separators are widely used to separate iron minerals from non-magnetic materials.
2. Gravity Separation
Equipment such as jigs, spirals, and shaking tables separate ore based on density differences.
3. Flotation
Flotation uses chemical reagents to selectively separate iron minerals from gangue material, especially for low-grade ores.
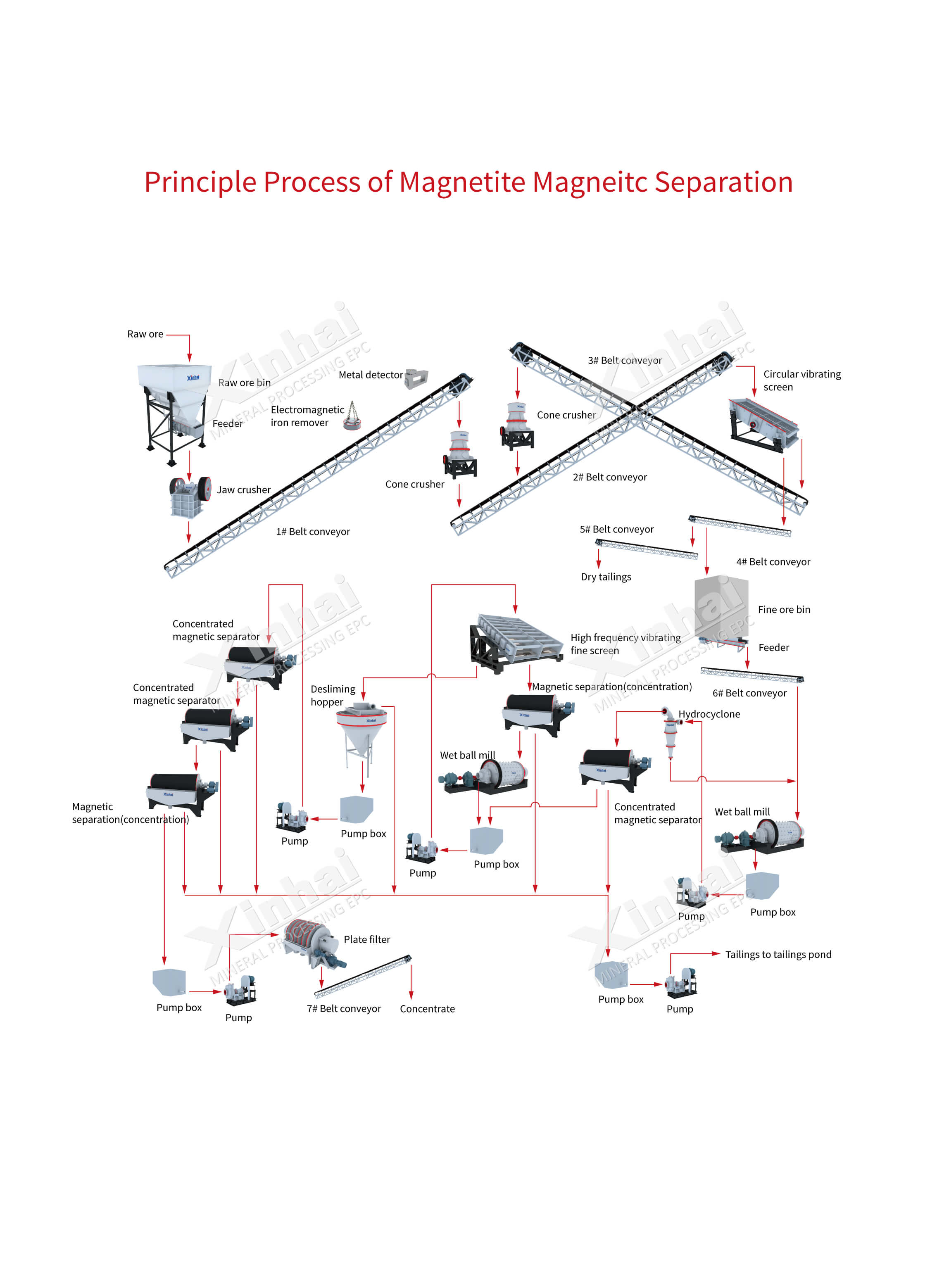
The principle flow of magnetic separation process for magnetite
06Step 5: Dewatering and Drying
BackAfter beneficiation, the iron ore concentrate contains excess water. Dewatering equipment such as thickeners, filters, and vacuum drums removes moisture.
In some cases, thermal dryers are used to achieve the desired moisture content for transportation or pelletizing.
Dewatering improves:
Handling and transport efficiency
Storage stability
Downstream processing performance
07Step 6: Pelletizing or Sintering (Optional)
BackDepending on the final application, iron ore concentrate may undergo pelletizing or sintering. This step converts fine particles into larger, uniform shapes suitable for blast furnaces or direct reduction processes.
Pelletizing improves:
Furnace efficiency
Material handling
Product consistency
08Step 7: Final Product Handling and Transport
BackThe final processed iron ore—whether concentrate, pellets, or sinter—is stored, stockpiled, and transported to steel plants by rail, ship, or conveyor systems.
At this point, the iron ore processing flow chart is complete, and the material is ready for steel production.
09Benefits of an Efficient Iron Ore Processing Flow Chart
BackA well-designed iron ore processing flow chart offers several advantages:
Higher iron recovery rates
Lower operating costs
Reduced environmental impact
Improved product quality
Better energy and water efficiency
10Conclusion
BackUnderstanding the iron ore processing flow chart step by step is essential for optimizing mining operations and improving overall productivity. From mining and crushing to beneficiation and final product handling, each stage plays a crucial role in producing high-quality iron ore for the steel industry.
By continuously refining processing techniques and adopting modern technologies, mining operations can achieve greater efficiency, sustainability, and profitability.
 +86 182 3440 3483
+86 182 3440 3483 yanzhang19990421@gmail.com
yanzhang19990421@gmail.com




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now