Cyanide vs. Non-Cyanide Gold Leaching Which Is Better
 Laura
Laura
 Nov 21, 2025
Nov 21, 2025
 1134
1134
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!

gold leaching solutions
Gold leaching is a crucial step in gold extraction, and the choice of leaching method can significantly impact both recovery rates and environmental safety. Traditionally, cyanide has been the primary agent used in gold leaching, but concerns over toxicity have prompted the development of non-cyanide alternatives. This article explores the differences between cyanide and non-cyanide gold leaching, comparing their efficiency, cost, and environmental implications.
01 What Is Cyanide Gold Leaching?
BackCyanide gold leaching, also known as cyanidation, is the process of dissolving gold from ores using a cyanide solution. The reaction forms a soluble gold-cyanide complex that can be recovered through various methods such as activated carbon adsorption or zinc precipitation.
Advantages of Cyanide Leaching:
High gold recovery rates (up to 95% in most ores).
Well-established industrial process with decades of research and optimization.
Compatible with a wide range of ore types.
Disadvantages of Cyanide Leaching:
Highly toxic and hazardous to humans and wildlife.
Requires strict handling, storage, and disposal procedures.
Potential for catastrophic environmental contamination in case of leaks or spills.
02 What Is Non-Cyanide Gold Leaching?
BackNon-cyanide gold leaching uses alternative chemicals to dissolve gold from ores. Popular non-cyanide leaching agents include thiosulfate, thiourea, halide solutions, and bromine. These methods aim to reduce environmental and health risks associated with cyanide.
Advantages of Non-Cyanide Leaching:
Significantly lower toxicity compared to cyanide.
Reduced risk of environmental contamination.
Potentially safer for use in sensitive or small-scale mining operations.
Disadvantages of Non-Cyanide Leaching:
Generally lower gold recovery rates than cyanide.
Chemicals like thiourea or halides can be expensive and unstable.
Less established process, often requiring careful optimization for specific ores.
03 Cyanide vs. Non-Cyanide Gold Leaching: Key Comparisons
Back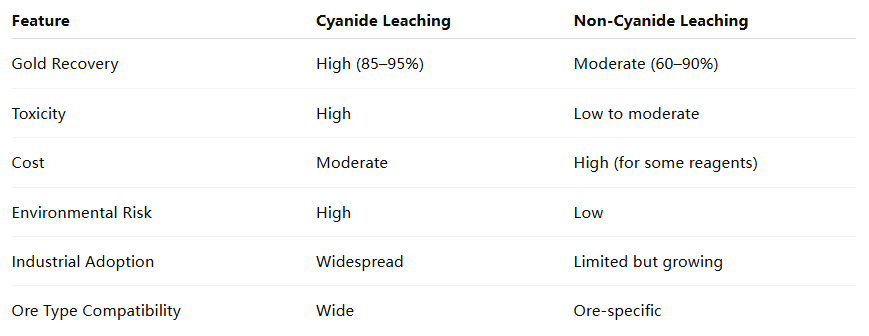
04 Which Method Is Better?
BackThe choice between cyanide and non-cyanide gold leaching depends on the priorities of the mining operation:
For maximum gold recovery: Cyanide leaching remains the industry standard due to its efficiency and proven results.
For environmental safety: Non-cyanide alternatives are preferred, especially in ecologically sensitive areas or for small-scale miners.
For cost considerations: Cyanide is generally cheaper in large-scale operations, while non-cyanide reagents can be more expensive but may reduce costs related to environmental compliance.
In practice, some operations combine methods or explore hybrid solutions to balance recovery, cost, and environmental responsibility.
05Conclusion
BackBoth cyanide and non-cyanide gold leaching have distinct advantages and limitations. Cyanide leaching excels in recovery and cost-effectiveness but carries significant environmental risks. Non-cyanide leaching offers safer, more eco-friendly alternatives, though often at the expense of efficiency and cost. The "better" choice depends on the ore characteristics, regulatory requirements, and environmental considerations of the mining operation.
 +86 182 3440 3483
+86 182 3440 3483 yanzhang19990421@gmail.com
yanzhang19990421@gmail.com




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now

















