Fluorite Processing Plant Cost Analysis
 zeki
zeki
 Oct 31, 2025
Oct 31, 2025
 572
572
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!
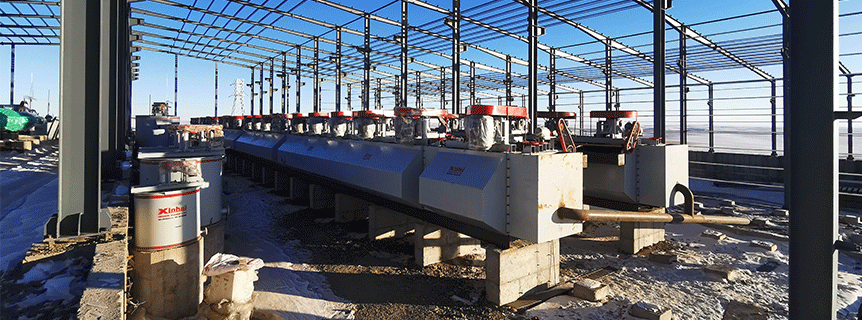
Mongolia 800tpd fluorite beneficiation plant
The cost of a Fluorite Processing Plant is a complex system engineering project, influenced by multiple factors including resources, technology, management, and policy. Successful cost control does not lie in simply reducing costs in individual areas, but rather in achieving optimization and synergy across the entire process through technological innovation and refined management. This builds a core cost advantage under intense market and environmental pressures.
01 One-time Plant Construction Investment
BackThis is the essential "hard cost" required to start the project, much like needing a foundation and materials to build a house.
Core Equipment: Includes a full production line of equipment such as crushers, ball mills, flotation machines, and dewatering machines. This is a major cost component, directly determining the plant's scale and capacity.
Buildings & Facilities: Requires construction of workshops, raw material storage, finished product storage, offices, etc.
Critical & Mandatory Item: Tailings Pond. This is for the safe storage of waste residues generated after beneficiation. Its design, construction, and compliance approval costs are high, but it is absolutely essential.
Intuitive Understanding: This is your "entry ticket," determining the basic scale and profile of your plant.
02 Permitting & Compliance Costs
BackBefore construction can begin, all necessary official permits must be obtained. This is a "soft cost," but it determines the project's legality.
Core Certificates: Mining rights license, business license, land use permit, etc.
Key Assessment: Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is paramount. It requires assessment by professional institutions and government approval to prove the project meets environmental standards. Related environmental facility investments also fall under this category.
Safety Permit: Work Safety Permit, ensuring the plant's design and management comply with national safety regulations.
Intuitive Understanding: This money is spent to make the project "legitimate," ensuring legal and compliant operation and avoiding future policy risks.
03 Daily Operating Costs
BackOnce the plant is built, these costs are incurred every day it operates. They directly determine the cost per ton of concentrate produced, impacting profit.
Electricity: Beneficiation is highly energy-intensive; electricity is the largest ongoing expense.
Labor: Wages and benefits for all personnel, from operators to management.
Reagents & Consumables: Special chemicals needed for the flotation process, and consumables like steel balls for grinding.
Equipment Maintenance: Routine upkeep and replacement of parts to ensure stable production line operation.
Intuitive Understanding: These are the plant's "daily expenses." The lower these are, the more price-competitive your product is in the market.
04 Raw Material & Transportation Costs
BackWithout ore, even the best plant cannot produce. This is a core component of the product cost.
Raw Ore Cost: The fundamental cost of acquiring the ore itself, whether from a company-owned mine (requiring amortization calculations) or purchased externally.
Transportation Fees: Includes two segments: the cost of transporting raw ore from the mine to the concentrator, and the logistics cost of delivering the processed concentrate to customers.
Intuitive Understanding: Raw ore is the "food," and transportation is the "blood vessels." The cost and quality of the "food," along with the efficiency of its "circulation," collectively determine the "fitness" of your product.
05 Reserve Funds & Hidden Costs
BackAny project may encounter unforeseen circumstances, so a portion of funds must be reserved as a buffer.
Construction Cost Overtuns: Budget overruns can occur during construction due to material price increases, engineering changes, etc.
Technical Debugging: The production line might not meet ideal performance indicators during the commissioning phase, requiring time and technical input for optimization.
Market Fluctuations: The ability to cope with price volatility in the fluorite market.
Intuitive Understanding: This money is your "safety cushion" or "insurance," ensuring the project ship doesn't capsize when encountering minor storms.
06 Summary & Recommendations
BackSimply put, your total investment = (1 + 2) One-time investment + (3 + 4) Ongoing costs + 5 Risk reserve.
Items 1 & 2 determine whether you can build a qualified plant and open it legally.
Items 3 & 4 determine how much money you actually make for each ton of product sold after the plant is operational.
Item 5 determines your project's ability to withstand risks.
 +86 182 3440 3483
+86 182 3440 3483 yanzhang19990421@gmail.com
yanzhang19990421@gmail.com




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now

















