Dry vs Wet Iron Ore Processing: Key Differences
 Laura
Laura
 Feb 21, 2026
Feb 21, 2026
 7
7
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!

Transportation of iron ore flotation cells
Iron ore processing is a crucial stage in the mining and steel industries. Choosing the right method—dry processing or wet processing—can significantly affect efficiency, recovery rates, operational costs, and environmental impact. This article explains the key differences between dry and wet iron ore processing, their applications, advantages, and limitations.
01What Is Iron Ore Processing?
BackIron ore processing involves extracting valuable iron minerals from raw ore and producing a high-grade concentrate for steelmaking. Depending on ore type, moisture content, and local conditions, processing can be conducted using dry or wet methods.
The main goal: maximize iron recovery while minimizing impurities and operational costs.
02Dry Iron Ore Processing
BackDry processing involves crushing, screening, and magnetic separation of ore without using water. This method is typically applied to high-grade, low-impurity iron ores.
1. Steps in Dry Processing
Crushing and Screening: Ore is reduced to a manageable size using jaw, cone, or impact crushers.
Magnetic Separation: Iron minerals are separated from gangue using magnetic separators.
Fine Grinding (Optional): Some ores may require additional grinding to achieve proper liberation.
Final Concentrate Handling: The dry concentrate is stored and transported for steelmaking.
2. Advantages of Dry Processing
Reduces water consumption
Lower operating costs
Simpler plant design
Avoids water-related environmental issues
3. Limitations
Less effective for low-grade or clay-rich ores
Dust generation can be a problem
Harder to achieve high purity compared to wet processing
03Wet Iron Ore Processing
BackWet processing uses water in combination with crushing, grinding, and separation techniques to remove impurities and recover iron minerals. This is the most common method for low- to medium-grade ores.
1. Steps in Wet Processing
Crushing and Screening: Ore is crushed and sized.
Grinding and Slurry Formation: Water is added to create a slurry for easier handling.
Separation: Magnetic separation, gravity separation, or flotation is used to concentrate iron minerals.
Dewatering: Excess water is removed using thickeners, filters, or vacuum drums.
Final Product Handling: The wet concentrate may be dried, pelletized, or transported as slurry.
2. Advantages of Wet Processing
Higher recovery rates for low-grade ores
Produces finer particle liberation
Effective for clay-rich or sticky ores
Easier dust control
3. Limitations
Higher water consumption
More complex plant design
Increased energy usage
Wastewater management required
04Key Differences Between Dry and Wet Processing
Back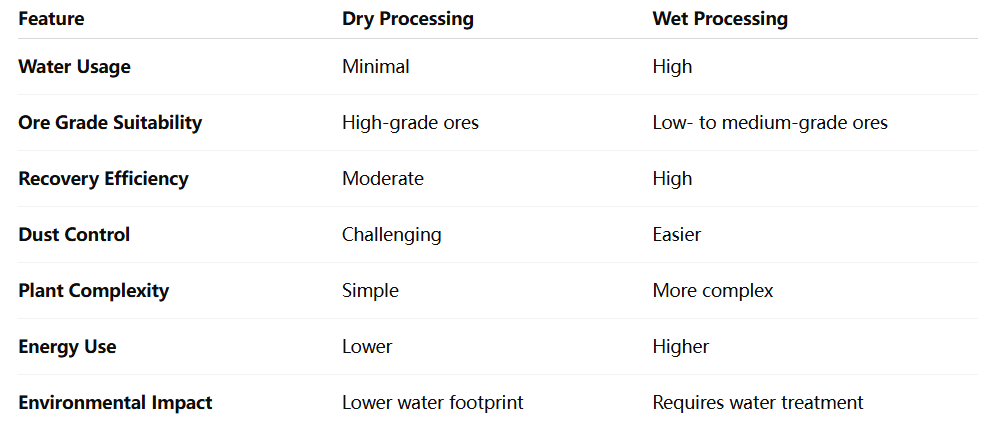
Key Differences Between Dry and Wet Processing
05Which Method Should You Choose?
BackThe choice between dry and wet processing depends on:
Ore characteristics (grade, moisture, impurities)
Availability of water and environmental regulations
Plant size and capital cost constraints
Desired recovery rates and concentrate quality
Rule of thumb: High-grade ores with low impurities often use dry processing, while low-grade or clay-rich ores require wet processing.
06Emerging Trends in Iron Ore Processing
BackHybrid Systems: Combining dry and wet methods to optimize efficiency
Water Recycling: Reducing freshwater use in wet processing
Advanced Magnetic Separation: Improving dry process recovery
Automation: Enhancing control and efficiency in both methods
07Conclusion
BackUnderstanding the key differences between dry and wet iron ore processing is essential for selecting the right method for your ore type and operational conditions. Each method has advantages and limitations, and careful evaluation ensures optimal recovery, lower costs, and environmental compliance.
A well-planned processing strategy, whether dry, wet, or hybrid, is critical to achieving consistent, high-quality iron ore production.
 +86 182 3440 3483
+86 182 3440 3483 yanzhang19990421@gmail.com
yanzhang19990421@gmail.com




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now

















