From Mine to Concentrate: Stibnite Processing Explained
 Laura
Laura
 Dec 26, 2025
Dec 26, 2025
 322
322
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!

aerial view of the ore processing plant
Stibnite (Sb₂S₃) is the primary mineral source of antimony, a critical element used in flame retardants, batteries, alloys, semiconductors, and chemical industries. As high-grade antimony deposits become scarce, efficient stibnite processing has become essential to maximize recovery and produce high-quality antimony concentrates.
This article explains the complete stibnite processing journey—from mine to concentrate, covering mining, crushing, beneficiation, and concentrate handling in a clear, step-by-step manner.
Understanding Stibnite and Its Importance
Stibnite is a sulfide mineral of antimony characterized by its high density, metallic luster, and relatively low hardness. It is commonly associated with quartz, calcite, pyrite, and other sulfide minerals.
Why Stibnite Processing Matters:
Stibnite is the main commercial source of antimony
Antimony demand is rising across multiple industries
Efficient processing improves recovery and reduces operating costs
Understanding stibnite's mineralogical properties is key to designing an effective processing flow.
01Step 1: Stibnite Mining and Ore Handling
BackThe stibnite processing cycle begins with ore extraction, typically through open-pit or underground mining depending on deposit depth and structure.
Key Mining Considerations:
Ore grade and vein thickness
Rock hardness and fragmentation
Dilution control to maintain feed quality
After mining, the run-of-mine (ROM) ore is transported to the processing plant for further treatment.
02Step 2: Crushing of Stibnite Ore
BackCrushing reduces large ore fragments into smaller particles suitable for grinding and beneficiation.
Common Crushing Equipment:
Jaw crushers (primary crushing)
Cone or impact crushers (secondary crushing)
Controlled crushing is important because stibnite is relatively soft and brittle; excessive crushing can produce fines that negatively impact recovery.
03Step 3: Grinding and Classification
BackAfter crushing, the ore undergoes grinding and classification to liberate stibnite crystals from gangue minerals.
Typical Equipment:
Ball mills or rod mills
Hydrocyclones or classifiers
Proper grinding fineness is critical. Under-grinding leads to poor liberation, while over-grinding creates slime losses during flotation.
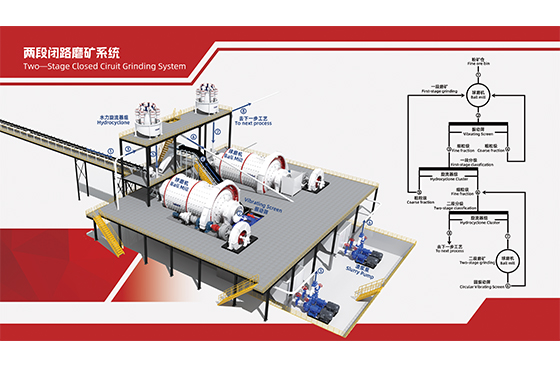
Two-Stage Closed Ciruit Grinding System
04Step 4: Gravity Separation in Stibnite Processing
BackDue to its high specific gravity, gravity separation is often used as a pre-concentration step in stibnite processing.
Common Gravity Separation Methods:
Jigging
Shaking tables
Spiral concentrators
Gravity separation removes coarse gangue early, reducing the load on flotation circuits and improving overall efficiency.
05Step 5: Flotation Beneficiation of Stibnite
BackFroth flotation is the most widely used method for producing high-grade antimony concentrates from stibnite ores.
Flotation Process Overview:
Collectors selectively bind to stibnite particles
Frothers create stable air bubbles
Depressants suppress unwanted sulfide and silicate minerals
Common Flotation Reagents:
Xanthates and dithiophosphates (collectors)
Pine oil or MIBC (frothers)
Lime, sodium silicate, or starch (modifiers)
Flotation allows precise control over concentrate grade and recovery.
06Step 6: Concentrate Thickening, Dewatering, and Drying
BackAfter flotation, the antimony concentrate contains excess water and must be thickened and dewatered.
Dewatering Equipment:
Thickeners
Vacuum filters
Filter presses
The final drying stage reduces moisture content, making the concentrate suitable for smelting or export.
07Step 7: Tailings Management and Environmental Control
BackResponsible tailings management is a critical component of modern stibnite processing plants.
Environmental Measures Include:
Tailings thickening and safe disposal
Water recycling systems
Dust and emissions control
Monitoring antimony levels in wastewater
Sustainable practices help meet regulatory requirements and reduce environmental impact.
08Key Challenges in Stibnite Processing
BackStibnite processing presents several technical challenges, including:
Fine-grained mineral dissemination
Sensitivity to over-grinding
Complex ore compositions with multiple sulfides
Advanced process control and reagent optimization are often required to overcome these challenges.
09Conclusion
BackThe journey from mine to concentrate in stibnite processing involves a carefully coordinated series of steps, including mining, crushing, grinding, gravity separation, flotation, and dewatering. Each stage plays a crucial role in producing high-quality antimony concentrate with maximum recovery.
By understanding stibnite's mineral characteristics and applying the right processing technologies, mining operations can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and meet the growing global demand for antimony.
 +86 182 3440 3483
+86 182 3440 3483 yanzhang19990421@gmail.com
yanzhang19990421@gmail.com




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now

















